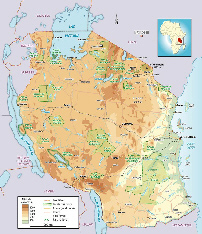
Geography
Tanzania is the largest country of East Africa. Much of the country is formed by the highlands where the altitude ranges around 1500 m.
- Mountains: two peaks, Mount Kilimanjaro (5895 m) and Mount Meru (4,566 m) rush to the north, bordering with Kenya.
- The steppes and savannas: 64% of the country consists of steppes and savanna grasses (steppe + = few scattered trees, savanna). That's bush.
- Forests: even though 36% of its total area is forest, to discover the true equatorial rainforest is in the former Zaire (now Democratic Congo said) that he must go, not Tanzania.
There are still some forests as interesting rainforest (or rain) mountain can grow up to 3000 m altitude.
It covers the slopes of Mount Meru, Kilimanjaro, and the slopes of Ngorongoro Crater.
There are also gallery forests, a type of long dense forests consisting of tropical trees (palm trees sausage ...) which fringe the banks of rivers or lakes. But the benefit of crop, forest retreats each year.
Different geographical areas
- The Tanzanian coast: the coastal plain, deep sixty kilometers, offers relatively poor soils. .
Mangrove occupies the flooded areas of the sea or river deltas.
- The tops of the Centre: the landscapes vary.
Maasai steppe is common and usually does not have trees. African savanna (also known as bush) is sparse and dotted with acacia, euphorbia, palms, baobabs ...
- North of the country: the most mountainous region, where also the largest national parks most visited.
- The West: Lake Tanganyikais a deepest lake in the world, discovered in 1858 by explorers Speke and Burton, is the longest freshwater lake in the world (32 000 km2, 675 km long and 50 km wide) and the second by its depth (1434 m) after Lake Baikal (Russia). It flows into the River Zaire River Loukouga















.png)